|
Mirror formula |
1/V + 1/U = 1/F |
|
Magnification by Mirrors |
M = H’/H = - V/U |
|
Refractive Index |
U = V1/V2 |
|
Absolute Refractive Index |
U = C/V |
|
Lens Formula |
1/V – 1/U = 1/F |
|
Magnification by Lenses |
M = H’/H = V/U |
|
Power of Lens & SI unit |
P = 1/F, SI unit Dioptre |
|
Concave Mirror forms Real and Inverted Image except
when object is between pole and focus |
Convex Mirror always forms Virtual and erect Image |
|
Concave lens always forms Virtual and Erect image |
Convex lens forms real and virtual image except when
object is between optical centre and F1 |
|
If Power of Lens is +ve, It is Convex |
If Power of Lens is -ve, It is concave |
|
Plane mirror has the
focal length of Infinity |
Spherical mirrors and lenses have many uses |
Ans: Spherical mirror is the part of sphere with curved reflecting surface.
These are of two types:
1. Concave mirror: It is type of spherical mirror whoes outer surface is polished and reflection takes place from inside.
It is also called convergent mirror.
2. Convex mirror: It is type of Spherical mirror whoes inner surface is polished and reflection takes place from outside.
It is also called divergent mirror.
Ans:
Concave Mirror:
1. It is used as shaving mirror.
2. It is used in torches and headlights of cars.
3. It is used in telescopes.
Convex Mirror:
1. It is used in street lamps.
2. It is used as side view mirror in cars.
Q. What are properties of image formed by plane mirror?
Ans:
1. The image is Virtual and erect.
2. The image is of same size as that of object.
3. The image is as far behind the mirror as the object is infront of it
4. The image is laterally inverted
Q. What is reflection? What are the laws of reflection?
Ans: The bouncing back of rays of light when they falls on surface is called as reflection of light.
Reflection is smooth on plane polished surface or diffused on uneven surface.
1. The Incident Ray, Reflected Ray and Normal lie in the same plane.
2. The angle of Incidence <i is equal to angle of reflection <r.
Ans. Mirror Formula: Mirror formula is the relation between Object Distance (U), Image Distance (V) and focal length (F) of mirror.
It is given by,
Magnification: Magnification by spherical mirror is defined as ratio of height of image (h') to height of object (h), i.e,
M = h'/h = -V/U
Q. Describe the Size, Nature and Position of Image formed by Concave mirror?
Ans: The concave mirror forms images depending of the position if object.
1. Object at Infinity: The image is formed on Focus (F). The image is very Dim, Real and Inverted
2. Object beyond Centre of Curvature (C): The image is formed between Focus (F)and Centre of Curvature (C). The image is Dim, Real and Inverted
3. Object at Centre of Curvature (C): The image is also formed at centre of curvature (C). The image is of same size, Real amd inverted.
4. Object between Centre of Curvature (C) and Focus (F): The Image is formed beyond centre of curvature (C). The image is large, Real and Inverted
5. Object at Focus (F): The image is formed at Infinite. The image is very large, Real and Inverted.
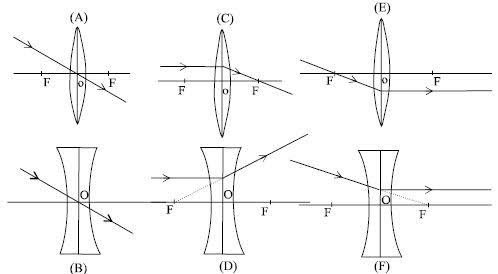
Q. Draw a ray diagram in each of the following cases to
show the formation of image when the object is placed:
i. Between Centre of Curvature and Principal focus of
concave mirror
ii. At the focus of concave mirror
iii. Between focus and pole of the concave mirror
Ans:
Q. Explain the Image formation by Convex mirror?
Ans: The Convex mirror forms following two images depending upon the position of object;
1. When the object is at Infinity:
The image is formed at the Focus (F).
The image is virtual, erect and very dim.
2. When the object is between Infinity and Pole:
The image is formed between pole and focus (F).
The image is virtual, erect and dim.
A. Pole
B. Centre of Curvature
C. Focus
D. Principle Axis
A. POLE: Pole (P) is the centre of Reflecting Surface.
B. Centre of Curvature: The centre of Curvature (C) is centre of sphere of which mirror is a part of. The distance between Pole and Centre of Curvature is the Radius of mirror.
C. Focus: Focus (F) is the point on principle axis where the rays of light meet after reflection. Distance between Focus amd Pole is called Focal Length
D. Principle axis: (P) It is straight line that connects Centre of Curvature, Focus and Pole of mirror.
Ans: When light enters from one medium to another, It bends towards the normal or away from it. This process is called refraction.
1. The Incident Ray, Refracted Ray and z normal are all in same plane.
2. The ratio of Sin of angle of incidence to Sin of angle of refraction is always constant. This is also called snells law.
Ans: Refractive Index is defined as Ratio of speed of light in Vacuum to the speed of light in a medium.
Refractive index measures the change in direction of light ray when it changes the medium
It is denoted by ų. It has no units.
Refractive index is given by=
Speed of light in Vaccum (C)
When light travels from one medium to another, It is relative refractive index.
Q. Explain Snell's Law.
Ans: Snell’s law is defined as “The ratio of the sine of the angle of incidence to the sine of the angle of refraction is a constant, for the light of a given colour and for the given pair of media”.
Snell’s law formula is expressed as:
Sin <i/ Sin <r = Constant = Refractive Index
Q. What is Spherical Lens? What are its types.
Ans: A spherical Lens is a transparent material whoes one or both surfaces are Spherical and bend the ray of light.
Lenses are of two types:
Convex lens: It converges the ray of light after passing through it.
Concave lens: It diverges the ray of light after passing through it.
Ans: Lens formula defines the relation between Image distance (V), Object Distance (U) and Focal Length (F) of the lens. i.e,
Magnification of lens defines the relation between ratio of height of image to height of object, i.e,
M = h'/h = V/U
Q. What is Power of Lens.
Ans: The Power of lens (P) is the ability of lens to converge or diverge the rays of light.
Lesser the focal length of lens, the more it converges or diverges the light. i.e,
P = 1/F
Its SI unit is dioptre, 1 dioptre means the power of lens whose focal length is 1 metres.
Power of Convex lens is Positive and power of Concave lens is negative.
Ans: The image formed by Convex lens depends on the position of object.
1. Object at Infinite: The image is formed at F2, The image is very dim, Real and inverted
2. Object beyond 2F1: The image is formed between F2 and 2F2. The image is dim, Real and Inverted.
3. Object at 2F1: The image is formed at 2F2. The image is of same size, Real and Inverted.
4. Object between 2F1 and F1: The Image is formed beyond 2F2. The image is large, Real and Inverted.
5. Object at F1: The image is formed at infinite. The image is very Large, Real and Inverted.
Ans: The concave lens forms following two images depending upon the position of object;
1. When object is at Infinity:
The image is formed at Focus (F1).
The image is virtual, erect and very dim.
2. When the object is between Infinity and Optical centre:
The image is formed between Optical centre and focus (F1).
The image is virtual, erect and dim.
Q.
Construct a ray diagram to illustrate the formation of a virtual image using:
I. A
converging Lens II. A diverging lens
What is
the difference between the two images formed above?
Ans: A
Converging lens forms a virtual image when the object is between Focus and
Optical center.
A diverging
lens always forms virtual image as shown below.
The
difference between both the images is that Converging lens (Convex lens) forms
larger image whereas Diverging lens (Concave lens) forms smaller image.
Q. State
three characteristics of the image formed by a Convex mirror?
Ans: The
characteristics of the image formed by a convex mirror are:
The image
formed is a virtual image.
The image
is formed behind the convex mirror.
The image
formed is smaller than the object.
Q. An
object 1 cm tall is placed 30 cm Infront of convex mirror of focal length 20
cm. Find the size and Position of the image formed by convex mirror.
Ans:
Given,
The mirror is a diverging mirror, i.e. convex mirror.
Height of the object 'ho' = 1 cm
Distance of the object from the mirror 'u' = -30 cm
Focal length of the convex mirror 'f' = 20 cm
We have to find the position of the image 'v', the height of the image
'h', and its magnification 'm'. Using the mirror formula, we get
1/f=1/v+1/u
1/20=1/v+ 1/−30
1/v=1/20+1/30
1/v = 3
+ 2
60
v =12 cm.
The image will be at a distance of 12 cm behind the mirror. Now, using
the magnification formula, we get
M =− v/u = − 12/−30
= 0.4
Thus, the image is virtual, erect, and smaller in size and its height
will be 0.4 cm
Ans:
The rules used for drawing ray diagrams for the formation of an image by a concave mirror are:
Rule 1: If the incident ray is parallel to the principal axis then the reflected ray passes through the focus of the concave mirror.
Rule 2: If the incident ray passes through the focus of the concave mirror, the reflected ray is parallel to the principle axis.
Rule 3: If the incident ray passes through the Centre of curvature of the concave mirror, the reflected ray is reflected back on the same path.

Ans:
The rules used for drawing ray diagrams for the formation of an image by a concave and convex lens are:
Rule 1: If the incident ray is parallel to the principal axis, it bends and passes through the Focus or appears to come from the Focus.
Rule 2: If the incident ray passes through the Focus of the lens, it bends and goes parallel to the principle axis.
Rule 3: If the incident ray passes through the optical centre of the lens, it does not bend and follows straight path.
Sol: Given,
F = - 20
V= - 15
U = ?
H= 5
We Have,
1/V – 1/U = 1/F
1/-15 - 1/U = 1/-20
-1/U = 1/-20 + 1/15
- 1/U = -3 + 4/ 60
-1/U = 1/60
U = - 60
Minus Sign indicates that object is placed on left of the lens, which always is the case.
Now, Magnification =
H’/5 = -15/-60
H’ = 1.25 cm.
Plus sign indicates that the image is erect and virtual.
Q. A Concave lens has focal length of 15cm. At which distance should the object from the lens be placed so that it forms an image at 10cm from the lens? Also find the magnification produced by the lens.
Ans: Given:
F = - 15
V = - 10
U = ?
M = ?
We know,
1/V – 1/U = 1/F
1/-10 – 1/U = 1/-15
1/U = - 3 + 2/30
1/U = - 1/30
U = - 30
Thus, object distance is 30 cm.
Now, Magnification, M = V/U
M = - 10/ -30
M = 10/30
M = 0.33
Q. Write Sign Convention for spherical mirrors
Ans: The sign conventions for Spherical mirrors are as following:
i. Object is always taken on the left side of mirror.
ii. All the distance taken on the left side of mirror are taken as negative
iii. All the distance taken on the right side of mirror are taken as positive
iv. All the heights that are erect are taken as positive
v. All the heights that are inverted are taken as negative
Q. An object of size 7.0 cm is placed at 27 cm Infront of
a concave mirror of focal length 18 cm. At what distance from the mirror should
a screen be placed so that a sharp focused image can be obtained? Find the size
and the nature of the image
Ans: Given,
U = - 27 cm
H = 7 cm
F = - 18 cm
We Know,
1/V + 1/U = 1/F
1/V + (-1/27) = -1/18
1/V - 1/27 = -1/18
1/V = -1/18 + 1/27
1/V = -3 + 2
/54
1/V = -1/54
V = - 54 cm
Therefore, the screen should be placed 54 cm far from the
mirror to obtain sharp image.
To know the size of Image, we know
H’/H = - V/U
H’/7 = - (-54)/-27
H’ = - 2 * 7
H’ = -14 cm.
The image will be 14 cm long. The minus sigh indicates
that the image will be inverted and real
Q. The radius of curvature of spherical mirror is 20 cm. What is its focal length.
Ans:
Radius of curvature = 20 cms
Focal length= R/2
= 20/2 = 10 cms
Therefore, Focal length is 10 cm
Q. A concave mirror produces three times magnified real image of object placed at 10 cm infront of it. Where is the image located?
Ans: Here,
Magnification (m) = 3
Object Distance (U) = -10
i.e, h'/h = -V/U
I.e, 3 = - V/-10
-V = -30
V = 30
So Image is 30 cm from the mirror.
As given, the mirror is concave and image is real, therefore image is in same side of mirror as that of object.
Q. The refractive index of diamond is 2.42. What is meaning of this statement?
Ans: This means speed of light in diamond is 1/2.42 times than in vaccum.
In other words, Light travels 2.42 times faster in vaccum than in diamond.
Q. What is power of concave lens of focal length 2 m.
Ans: Here, Focal Length (f)= - 2 m
Power of lens= 1/f
= 1/-2
= -0.5 D
Q. An object is placed at distance of 10 cm from Convex mirror of focal length 15 cm. Find position and nature of image?
Ans:
Here, Object distance (U)= -10
Focal length (F) = +15
Image distance= V
Using mirror formula,
1/V + 1/U= 1/F
1/V + 1/-10 = 1/15
1/V= 1/15 + 1/10
1/V = __2__+___3____
30
1/V = 5/30
V =30/5
V= 6
Positive sign shows the image is virtual, erect and 6 cm towards right of mirror.
Ans: Given,
M = - 3 (Real Image is inverted, thus its magnification
is -)
U = - 10
V = ?
We Know,
M = - V/U
-3 = - V/-10
V = - 30 cm
This shows Image is on the same side as that of Object and is 30 cm away from the Pole of Mirror.
Q. A ray of light travelling in Air enters obliquely into water. Does the light ray bend towards normal or away from the Normal?
Ans: Since the ray of light is travelling from optically rearer to denser medium, thus it will bend towards the Normal.
Q: Light enters from air to glass having refractive index 1.50. What is speed of light in glass ? (Speed of light in vacuum is 3 x 108 m/s
Ans: Given,
Refractive Index of Glass = 1.50
Speed of light in
Vacuum = 3 x 108 m/s
We Know,
U = Speed of light in Vacuum
Speed in Medium
1.50 = 3 x 108 / V
V = 3 x 108 / 1.50
Thus, Speed of light in Glass = 2 x 108
Q: A concave lens forms a real and inverted image of a needle at a distance of 50 cm from it. Where is the needle be placed in front of the convex lens if the image is equal to size of the object? Also find the power of lens.
Ans: Given:
V = 50
M = - 1
U = ?
F = ?
P = ?
We Know;
M = V/U
-1 = 50/U
U = - 50 cm.
1/F = 1/V – 1/U
1/F = 1/50 – 1/(-50)
1/F = 1 + 1/50
1/F = 2/50 or
F = 50/2
F = 25
Power = 1/F
F = 25 cm or 0.25 m (To calculate power of lens, Focal
length taken in meters)
P = 1/0.25
P = 4 D
Q. An object 5 cm in length is held 25 cm away from a converging lens of focal length 10 cm. Find the position, size and the nature of image formed.
Ans: Given;
H = 5
U = -25
F = 10
V = ?
H = ?
We Know;
1/F = 1/V – 1/U
1/10 = 1/V – 1/-25
1/V = 1/10 – 1/25
1/V = 5 – 2/50
1/V = 3/50
V= 50/3
V = 16.7 cm
Now, Magnification (M) = H’/H = V/U
H’ = H.V/U
H’ = 5 x 16.7/ -25
H’ = - 3.3 cm
This shows Image is Real, Inverted and Diminished and 16.7 cm away from the lens on the same side as that of object.
Q. A concave lens of focal length 15 cm forms an image 10
cm from the lens. How far is the object placed from the lens?
Ans: Given;
F = - 15
V = - 10
U = ?
We Know,
1/V – 1/U = 1/F
1/ -10 – 1/U = 1/-15
1/U = 1/-10 + 1/15
1/U = -3 + 2/3=
1/U = - 1/30
U = - 30
Thus, the object is 30 cm away from the lens.
Q. The magnification produced by a plane mirror is + 1.
What does this mean?
It also means the Image is virtual and erect.
Q. An object 5.0 of length is placed at a distance of 20
cm Infront of a convex mirror of radius of curvature 30 cm. Find the position
of the image, its nature and size.
Ans: Given,
H = 5
U = - 20
F = + 15 (i.e Half of Radius of Curvature)
V =?
H’ =?
We Know;
1/F = 1/V + 1/U
1/15 = 1/V + 1/ -20
1/V = 1/15 + 1/20
1/V = 4 + 3/ 60
1/V = 7/60
V= 60/7
V = 8.5 cm
Now, Magnification (m) = H’/H = - V/U
H’/5 = - 8.5/-20
H’ = 8.5 x 5/20
H’ = 2.14 cm
+ve sign indicates that the image is erect and thus
inverted.
Q. Find the focal length of a lens of power – 2.0 D. What
type of lens is this?
Ans: Given;
P = - 2.0
We Know P = 1/F
Or F = 1/P
F = 1/-2
F = - 0.5 m or - 50 cm
Negative sign means the lens is Concave.
Q. A doctor has prescribed a corrective lens of power +
1.5 D. Find the focal length of lens. Is prescribed lens diverging or
converging?
Ans: Given;
P = + 1.5 D
We Know that;
P = 1/F
Or F = 1/P
F = 1/1.5
F = 0.67 m or 67 cm
Q. An object 5.0 cm in length is placed at a distance of 20 cm Infront of a convex mirror of radius of curvature 30 cm. Find the position of its image, its nature and size.
Ans: Given;
H = 5
U = - 20
F = + 15 ( Focal length is half of Radius of curvature)
We Know,
1/V + 1/U = 1/F
1/V + 1/-20 = 1/15
1/V = 1/15 + 1/20
1/V = 4 +3/60
1/V = 7/60
V = 60/7
V = 8.6 cm
Now,
Magnification (m) = H’/H = - V/U
H’/5 = - 8.6/-20
H’ = -8.6 x 5/20
H’ = 2.15 cm
Thus, Image is 8.6 cm away from the mirror and is Virtual and erect and diminished.
Q: A lens has a focal length of 150 mm what kind of lens
is it and what is its power?
Ans: Given, F = +150 mm i.e, + 0.15 m
We know,
Convex lens has positive focal length, hence it is CONVEX
lens.
P = 1/F
P = 1/0.15
P = + 6.66 D
Ans:
Q. The image formed by a concave mirror is virtual, erect and larger than the size of object. What is the position of an object and where the image is formed?
Ans: The position of the Object is between the Pole and Principle Focus of the mirror.
The Image will be formed behind the mirror.
Q. Define principal focus of a concave mirror.
Ans: The principal focus of a concave mirror is a point on principal axis at which all the light rays parallel to it meet after reflection.
Q. The image formed by concave mirror is Real, Inverted and Larger than object. What is the position of the object?
Ans: In a concave mirror, when object is placed between focus and curvature of center, the image formed is real, inverted and larger than the object.
Q. Define centre of Curvature of a spherical mirror?
Ans: Centre of curvature of a spherical mirror is defined as the centre of the sphere of which the mirror is a part of.
In other words, it is the centre of the sphere from which the spherical mirror is sliced.
Q. A concave lens is also a diverging lens. Why?
Ans: Concave lens is also called diverging lens because it diverges all the rays of light away from its principal axis.
Q. Define principal axis of a spherical mirror.
Ans: Principal axis is the line passing through the pole, centre of curvature and focus of a spherical mirror.
Q. For what position of an object, a concave mirror forms a real image equal in size of object.
Ans: When the object is placed at Centre of Curvature of a concave mirror, The image formed is real and equal in size of object.
Q. Give any one condition when no refraction takes place.
Ans: The refraction will not take place under two conditions:
I. The refractive index of two mediums is equal.
II. The Angle of Incidence is 0.
Ans: Refraction is caused when the rays of light travels from rearer to denser medium or vice versa.
Q. Convex lens is also called converging lens. Why?
Ans: Convex lens is also called converging lens because it converges all the rays of light towards its focus.
1. Water 2. Glass 3. Plastic 4. Clay
Ans: Clay
1. Between Principal focus and centre of Curvature
2. At centre of curvature
3. Beyond Centre of curvature
4. Between Pole and principal focus
Ans: Between Pole and Principal focus
Q. Where should a object be placed infront of convex lens to get real image of size of object?
1. At principal focus
2. Twice the focal length
3. At infinite
4. Between optical centre and principal focus
Ans: Twice the focal length of lens.
1. Concave
2. Convex
3. Mirror is concave, Lens is convex
4. Mirror is convex, Lens is concave
Ans: Concave
Q. No matter how far you stand from a mirror, your image appears erect. The mirror is likely to be:
1. Plane only
2. Concave only
3. Convex only
4. Either Plane or convex
Ans: Either plane or Convex.
Q. Which of following lenses would you prefer to use while reading small letters in a dictionary?
1. A concave lens of focal length 50 cm
2. A convex lens of focal length 50 cm
3. A convex lens of focal length 5 cm
4. A concave lens of focal length 5 cm
Ans:
A convex lens of focal length 5 cm
1. Zero 2. Infinity 3. Finite 4. None
Ans: Infinity.
Q. Which mirror is used in headlight of car
Ans: Concave mirror
Ans: Concave mirror.
Q. Which mirror is used as side and rear view mirror?
Ans: Convex mirror
Ans: Concave mirror.
Ans: Concave mirror.
Q. Convex mirrors are commonly used as:
(A) Shaving mirror (B) Rear-view mirror (C) Headlight mirror
(D) All of these
Ans: (B) Rear-view mirror
Q. The refractive index of diamond is 2.42. What is the meaning of this statement?
Ans: It means light travels 2.42 times slower in diamond.
Ans: When focal length of lens is 1 meter, Its power is 1 dioptre.
Q. Object AB is placed at centre of Curvature of a concave mirror. The inverted image of the object will be formed at centre of curvature. Draw a ray diagram of it.
Ans:
Ans:
Refractive index of water is 1.33
Refreactive index of crown glass is 1.52
Q. A ray of light goes from water into air. Will it bend towards normal?
Ans: No, the ray of light will bend away from the normal.
Q. Name the mirror which can give an erect and enlarged image of an object.
Ans: The Concave mirror can give erect and enlarged image of an object when it is placed between Focus and Pole.
Q. Which type of lens has positive power?
Ans: Convex lens has positive power as its focus lies towards the right side of lens.
Q. A diverging lens has a focal length of 0.10 m. What is its Power?
Ans: Power of Lens= 1/Focal length.
= 1/-0.10
= - 100/10
= - 10
Q. The power of lens is + 2.5 D, what kind of lens it is and what is its focal length?
Ans: Since the power of lens is +, the lens should be Convex.
Its focal length will be given as
1/F = 2.5
F = 1/ 2.5
F = 0.40 m
Q. A concave lens produces an image 20 cm from the lens of an object placed 30 cm from the lens. Find the focal length of the lens.
Ans: Here, V = - 20 , U = -30
We have,
1/V – 1/U = 1/F
1/-20 – 1/-30 = 1/F
1/-20 + 1/30 = 1/F
-3 + 2 = 1/F
60
-1/60 = 1/F
F = - 60
Q. Which type of mirror could be used as a shaving mirror?
Ans: The Concave mirror is used as a shaving mirror as it produces enlarged and erect image when the object is between Focus and Pole.
Q. Name the phenomenon due to which swimming pool appears less deep that it really is.
Ans: The Swimming pool appears less deep due to the phenomenon of Refraction.
Q. Which type of lens are thinner in the middle than at the edges?
Ans: Concave Lens are thinner in the middle than the edges.
Q. Name the mirror which gives an erect and diminished image of an object.
Ans: Convex mirror gives erect and diminished image of an object.
Q. A ray of light passes from air to glass, Is the angle of refraction greater or less than angle of Incidence?
Ans: When a ray of light passes from air to the glass, it will bend towards the normal. Hence, the angle of refraction is less than the angle of Incidence.
Q. Which type of lens is thicker in middle than at the edges?
Ans: Convex lens is thick in the middle than at the edges.
Q. The image formed by a concave mirror is observed to be virtual, erect and larger than the object. Where should be the position of the Object?
Ans: The object should be placed between Pole (P) and Focus (F) of the concave mirror.
Q. There is a Spherical mirror having the radius of curvature of 20 cm. What is its focal length?
Ans: The focal length is half of the radius of curvature. Therefore, Radius of curvature will be 10 cm.
Q. Absolute refractive index of Kerosene, turpentine and water are 1.44, 1.47 and 1.33 respectively. In which of these does light travel fastest?
Ans: The speed of light is inversely proportional to the refractive index. Therefore, the light travels fastest in water which has lowest refractive index of three.
Q. A ray of light traveling in air enters obliquely into water. Does the light ray bend towards the normal or away from the normal?
Ans: Since the ray of light is travelling from rarer to denser medium. Therefore, it will bend towards the normal.
Q. The focal length of a plane mirror is:
a) 0 b)
infinite c) 25 cm d) -25 cm
Ans: b) Infinite
Q. When the object is placed beyond centre of curvature of a concave mirror, the image formed will be:
a. Erect and Dim b. Erect and Magnified c. Inverted and Dim d. Inverted and Magnified
Ans: c. Inverted and Dim
Q. The image formed by a concave mirror is observed to be virtual, erect and magnified. Where should be the position of the object?
Ans: The object shall be placed between the Pole and the Focus of the concave mirror.
Q. A person cannot see distant objects kept beyond 2 m. This defect can be corrected by using a lens of power:
a. +0.5D b. -0.5D c. +0.2D d. -0.2D
Ans: b. -0.5D
Hint: The person is suffering from Myopia and hence needs a concave lens of power -0.5 D to correct the problem.
Q. A spherical mirror and a thin spherical lens have each a focal length of – 15 cm. The mirror and the lens are likely to be:
a. Both Concave b. Both Convex
c. The mirror is concave and the lens is convex
d. The mirror is convex and the lens is concave
Ans: c. The mirror is concave and the lens is convex
Q. Where should an object be placed Infront of a convex lens to get a real image of the size of the object?
Ans: The object should be placed at the principal focus (2F1) of the convex lens
Q. The focal length of a concave lens is 100 cm. Calculate its power in Dioptres:
a. 1 D b. 0.5 D c. 2 D d. 0.2 D
Ans: a. 1 D
Q. No matter how far you stand from the mirror, your image appears erect. The mirror is likely to be:
a. Plane b. Concave c. Convex d. Either Plane or Convex
Ans: d. Either Plane or Convex
Q. The power of concave lens is 0.5 D. Its focal length will be:
a. 100 cm b. 200 cm c. 150 cm d. 250 cm
Ans: b. 200 cm
Q. Define Radius of curvature of a spherical mirror.
Ans: Radius of Curvature is the distance between Centre of Curvature and the Pole of the spherical mirror.
Q. The image formed by a concave mirror is real, inverted and of the same size as the object. What is the position of the object?
Ans: The position of the object is at the Centre of Curvature.
Q. The refractive index of Diamond is
(a) 1.77 (b) 1.65 n (c) 2.42 (d) 2.13
Ans: (c) 2.42
Q. No matter how far you stand from a mirror your image appears erect. The mirror is likely to be
(a) Plane (b) Convex (c) Concave (d) Either plane or convex
Ans: (d) Either plane or convex
Q. A ray of light passing through optical centre of a concave lens.
(a) bends towards normal (b) bends away from normal (c) doesn't bend at all (d) None of the above
Ans: (c) doesn't bend at all
Q. When light enters a medium where its speed increases. It will bend:
(a) Randomly (b) Towards the normal (c) Away from the normal (d) Along the normal
Ans: (c) Away from the normal
Q. Define Regular reflection?
Ans: Regular reflection is a type of reflection which occurs on plane polished surfaces.
Q: Assertion (A) The height of an object is always considered positive
Reasons (R) An object is always placed above the principal axis in upward direction.
Ans: A and R are true and R is correct explanation of A














.jpeg)














Really a painstaking effort carried out by one of our brilliant teachers.
ReplyDeleteKudos to U , Fawad sir.
Thank you sir 😊😊😊
Deletesir do you take tuitions any where
ReplyDelete